WorkManager is an API to schedule deferrable, asyncronous jobs. This is one of the JetPack's best component and it's released only one week ago. Now I want to introduce it in a nutshell. To be honest, I've been waiting for a library like this FOR YEARS.
Test Environment:
- Windows 7 64Bit
- Android Studio 3.3.2
- Java 8
Add the WorkManager dependencies:
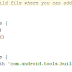
Open your project level build.gradle, and put into the repositories before all sub elements like this:
As a next step, you should add the library to your app level build.gradle:
The second is required only if you want to create tests for your WorkManager classes. Press "Sync now" to download dependencies.
Create a Worker
Worker is a runnable WorkManager based task. You don't have to worry about starting or managing runner threads, because everything is handled by WorkManager. I'll create an example, which downloads a remote JSON file. I'll use Retrofit2 as a HTTP client.
package ...;
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.work.Worker;
import androidx.work.WorkerParameters;
public class JSONLoaderWorker extends Worker {
JSONLoaderWorker(
@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull WorkerParameters params) {
super(context, params);
}
@Override
public Result doWork() {
// TODO Impl logic
return Result.success();
}
}
As you can see, when you create a new Worker, you have to override the onWork() method, which contains the concrete task, and it returns with a Result object, which has 3 possible output:
- Use Result.success(), when your job run successfully, without any problem.
- Use Result.failure(), when your job failed, and you don't want to restart it immediately after the failure.
- Use Result.retry(), when the job needs to be retried later.
Implement the Worker logic
As I mentioned, the Worker'll download a JSON file via Retrofit2. You can check it here:
So, if you don't have it, add Retrofit2 as a dependency in your app level build.gradle:
Then press "Sync now".
Next, open the AndroidManifest.xml, and add the INTERNET permission to your app:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
Without this, your app will not be able to connect to the internet.
Ok, it's time to implement the Retrofit components. First, create a Config file, which'll contain some necessary information:
public class Config {
public static final String LOG_TAG = "WorkManager Demo Part 1";
public static final String JSON_URL = "http://mysafeinfo.com/api/";
}
Then, we have to create the DTO:
public class King {
private long id;
private String nm;
private String cty;
private String hse;
private String yrs;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getNm() {
return nm;
}
public void setNm(String nm) {
this.nm = nm;
}
public String getCty() {
return cty;
}
public void setCty(String cty) {
this.cty = cty;
}
public String getHse() {
return hse;
}
public void setHse(String hse) {
this.hse = hse;
}
public String getYrs() {
return yrs;
}
public void setYrs(String yrs) {
this.yrs = yrs;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "King{" +
"id=" + id +
", nm='" + nm + '\'' +
", cty='" + cty + '\'' +
", hse='" + hse + '\'' +
", yrs='" + yrs + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Let's create a Retrofit helper class, a singleton, which'll responsible for managing the Retrofit instance:
import android.content.Context;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import okhttp3.OkHttpClient;
import retrofit2.Retrofit;
import retrofit2.converter.gson.GsonConverterFactory;
public class RetrofitClient {
private static final String DATE_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss";
private static RetrofitClient instance;
final Retrofit retrofit;
private RetrofitClient(Context context) {
final OkHttpClient.Builder client = new OkHttpClient.Builder();
client.connectTimeout(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
client.readTimeout(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
client.writeTimeout(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
final Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().setDateFormat(DATE_FORMAT).create();
retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder().client(client.build()).baseUrl(Config.JSON_URL)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create(gson)).build();
}
public static RetrofitClient getInstance(Context context) {
if(instance == null) {
instance = new RetrofitClient(context);
}
return instance;
}
public Retrofit getRetrofit() {
return retrofit;
}
}
Now we'll create the Retrofit interface, which'll download the data:
import java.util.List;
import retrofit2.Call;
import retrofit2.http.GET;
public interface GetDataService {
@GET("data?list=englishmonarchs&format=json")
Call<List<King>> listKings();
}
Finally we have to use the Retrofit in our Worker class:
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import android.util.Log;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import androidx.work.Worker;
import androidx.work.WorkerParameters;
import retrofit2.Response;
public class JSONLoaderWorker extends Worker {
// (1) Add the endpoint as a private class variable
private GetDataService endpointService;
JSONLoaderWorker(
@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull WorkerParameters params) {
super(context, params);
// (2) Initialize the variable with the RetrofitClient
endpointService = RetrofitClient.getInstance(context).getRetrofit().create(GetDataService.class);
}
@Override
@NonNull
public Result doWork() {
Log.i(Config.LOG_TAG, "Worker started");
try {
// (3) Call the endpoint
Response<List<King>> response = endpointService.listKings().execute();
List<King> resultList = response.body();
if(resultList != null) {
for(King king : resultList) {
Log.d(Config.LOG_TAG, king.toString());
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(Config.LOG_TAG, "Exception occured: " + e.getLocalizedMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
return Result.failure();
}
return Result.success();
}
}
And that's it.
Run the Worker
Ok, you have a Worker, but it's not running, it needs to be scheduled. One time Workers can scheduled the following way:
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.work.OneTimeWorkRequest;
import androidx.work.WorkManager;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
OneTimeWorkRequest configCheckerWorkRequest = new OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(
JSONLoaderWorker.class)
.build();
WorkManager.getInstance().enqueue(configCheckerWorkRequest);
}
}
If you start your application, you can find the downloaded data in your Logcat console:
Cancel the Worker
If you want to stop the running Worker, you can do it like this:
WorkManager.cancelWorkById(configCheckerWorkRequest.getId());
If you do not have the reference to the WorkerRequest, you can cancel it by the tag. If you want to do it on this way, first you should set a unique tag for this request:
When you cancel a Worker by tag, the WorkManager will cancel all Worker which has the same tag:
OneTimeWorkRequest configCheckerWorkRequest = new OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(JSONLoaderWorker.class)
.addTag("unique_tag")
.build();
.build();
When you cancel a Worker by tag, the WorkManager will cancel all Worker which has the same tag:
WorkManager.cancelAllWorkByTag("unique_tag");
Summary
You can find the whole project on GitHub:
In the next article, we'll discuss the recurring Workers and constraints.